A Common Strain of Dyspnea
Cassie Davenport, ACNP
Intermountain Medical Center
Murray, UT
Case:
A 42 year old male presents to the emergency department with progressive dyspnea x 4 days. He is tachycardic and tachypneic. Labs demonstrated moderate leukocytosis, positive troponin, and elevated BNP.
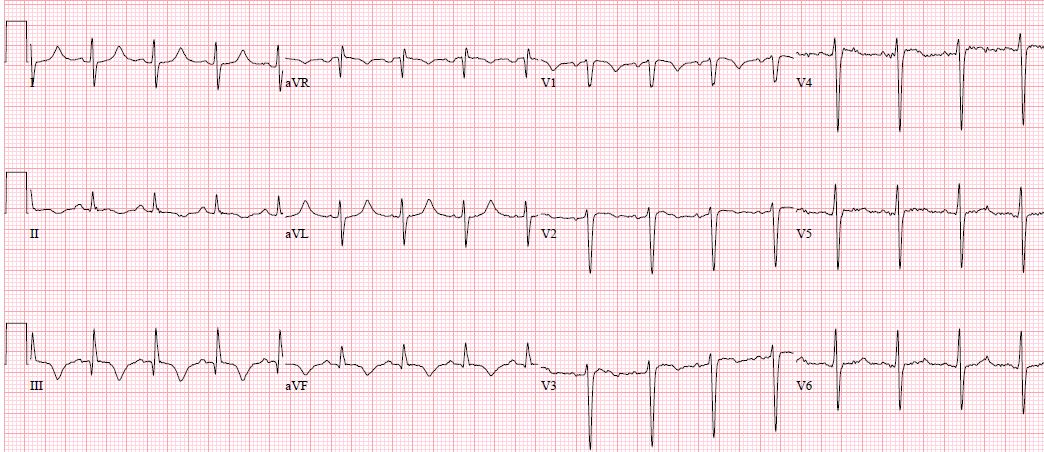
Question:
What does this EKG demonstrate?
S1 Q3 T3 pattern
Though EKG changes arenonspecific and with limited value diagnostically, they are associated with a poorer prognosis (i.e. new right bundle-branch block, atrial arrhythmias, inferior Q waves, right axis deviation ST changes or T wave inversions, s1q3t3 pattern). They are seen in less than 10 percent of pulmonary embolism patients, and only half of patients with massive pulmonary embolism. This finding is not sensitive (54%) nor specific (62%). Causes of acute right heart strain other than pulmonary embolism can also this pattern.
Acute RV strain can cause slow R wave progression and precordial T wave inversions. It may also be associated with a QR complex in V1/V2 in which the precise mechanism has not been determined. Acute PE can also cause ST elevation in right chest leads (rare) and is most likely related to RV ischemia.
The patient above also had right axis deviation and poor R-wave progression, and an incomplete right bundle branch block. Additional testing confirmed a saddle pulmonary embolism. Patient was treated with unfractionated heparin.
References:
-
Geibel A, Zehender M, Kasper W, et al. Prognostic value of the ECG on admission in patients with acute major pulmonary embolism. Eur Respir J 2005; 25:843.
-
Goldberger, A. (2015, May 12). Pathogenesis and diagnosis of Q waves on the electrocardiogram. Retrieved October 25, 2016, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pathogenesis-and-diagnosis-of-q-waves-on-the-electrocardiogram?source=search_result&search=S1Q3T3&selectedTitle=2~3
-
Ferrari E, Imbert A, Chevalier T, et al. The ECG in pulmonary embolism. Predictive value of negative T waves in precordial leads--80 case reports. Chest 1997; 111:537.
-
Rodger M, Makropoulos D, Turek M, et al. Diagnostic value of the electrocardiogram in suspected pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol 2000; 86:807.
-
Shopp JD, Stewart LK, Emmett TW, Kline JA. Findings From 12-lead Electrocardiography That Predict Circulatory Shock From Pulmonary Embolism: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Acad Emerg Med 2015; 22:1127.



